Understanding the Wolf Compared to Dog: Key Differences Explained
Overview
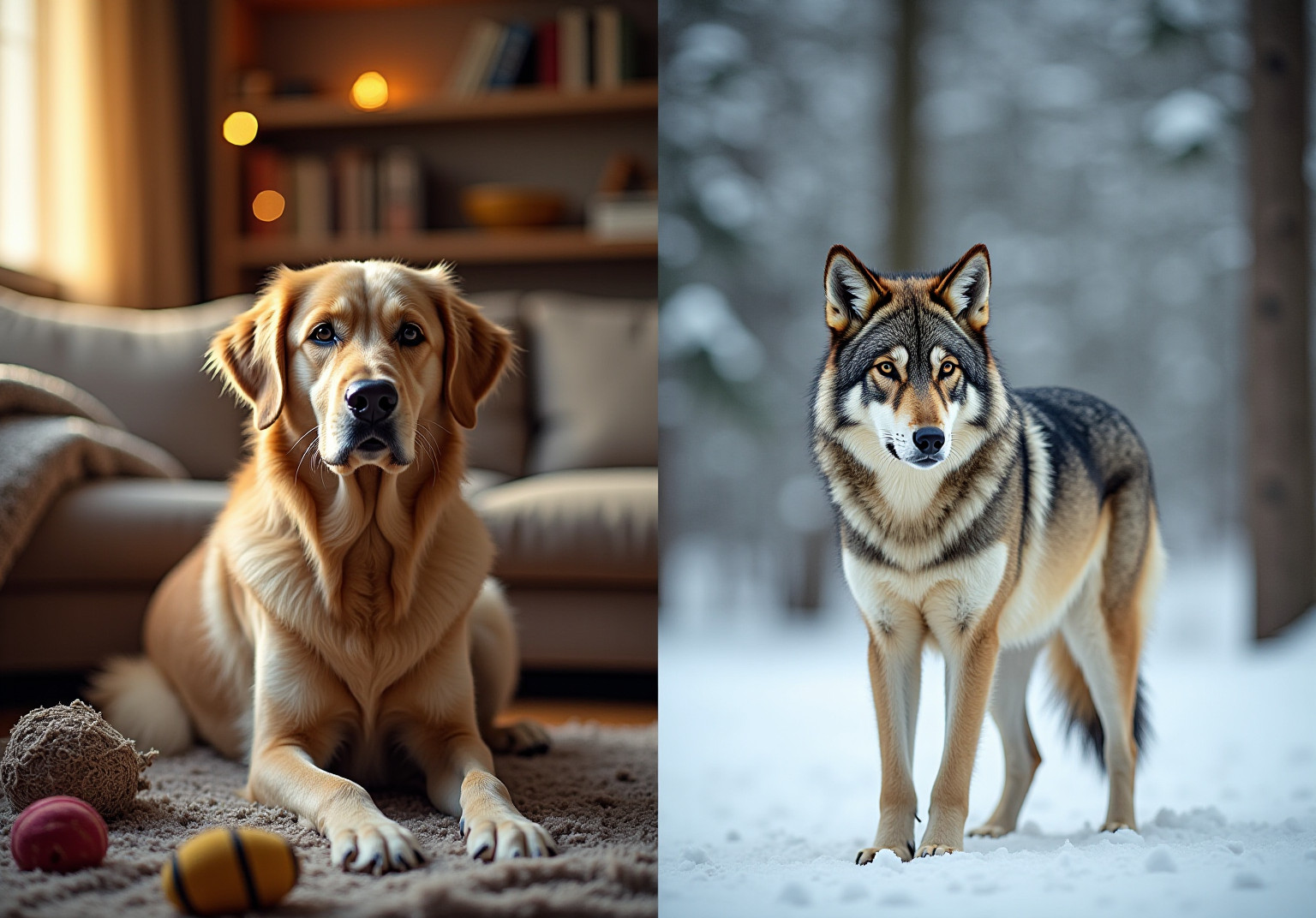
This article gently explores the key differences between your furry family members—wolves and dogs. It focuses on their evolutionary divergence, behaviors, and physical characteristics.
- While dogs have beautifully adapted to become more sociable and dependent on humans through domestication,
- wolves maintain strict pack hierarchies.
- They rely on instinct, showcasing distinct social structures and communication methods that reflect their survival needs in the wild.
Understanding these differences can help us appreciate the unique qualities of our pets and the importance of providing a nurturing environment for them.
Introduction
The intricate relationship between dogs and wolves unveils a captivating narrative of evolution and adaptation, inviting us to explore the deep connections we share with our furry family members. While both species share a common ancestor, their paths diverged dramatically, leading to distinct behaviors, social structures, and physical traits that reflect their unique lifestyles. This exploration delves into the fundamental differences between these two remarkable canids, revealing how domestication has shaped the canine’s dependency on humans and transformed their communication skills.
Yet, as we ponder these differences, we must consider:
- How do they influence the ways we bond with our beloved pets?
- What does it mean for their well-being in a human-centric world?
Understanding these aspects can help us create a nurturing environment that supports our pets’ needs and strengthens our relationship with them.
Fundamental Differences Between Dogs and Wolves
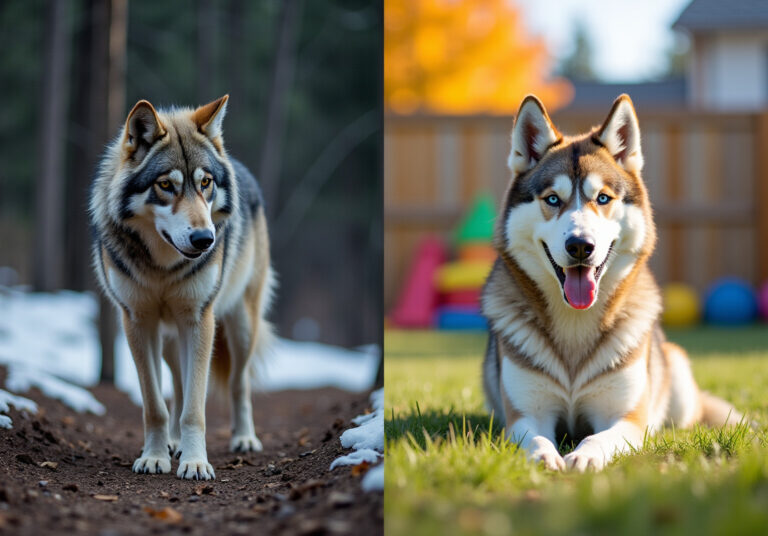
Dogs (Canis lupus familiaris) and wolves (Canis lupus) share a common ancestor, which reveals a fascinating connection and highlights the differences observed in wolf compared to dog. Over thousands of years of domestication, they have diverged significantly, adapting to their unique environments. While both species belong to the same family, their behaviors, community structures, and physical traits have evolved in ways that reflect their different lifestyles, similar to a wolf compared to a dog.
Wolves, primarily untamed, uphold strict pack hierarchies that are crucial for their survival. In contrast, our furry family members, the canines, have embraced more adaptable roles within our homes. This flexibility has made them more dependent on us for interaction and care, showcasing a beautiful bond that differs from the autonomy of wild canids. It’s heartwarming to see how canines have developed a distinctive ability to connect with people, a skill that is less pronounced in their wild counterparts, who rely more on instinct and group dynamics.
Research reveals that tamed canines exhibit smaller relative brain sizes compared to their wild relatives, with the absolute brain size of wolves being about 24.32% larger than that of canines with similar body mass. This difference reflects the evolutionary pressures that have uniquely shaped the species, including the wolf compared to dog. As canines evolved, they developed improved communication abilities with humans, essential for their integration into our lives. Meanwhile, wolves continue to preserve their innate behaviors necessary for survival in nature.
Furthermore, studies indicate that canines possess exceptional skills in communicating with humans, likely enhanced by domestication. This further emphasizes the cognitive differences between the two species, reminding us of the special place our pets hold in our hearts and homes. Understanding these differences can help us create a nurturing environment for our beloved companions, ensuring they thrive in our care.
Physical Characteristics: Dogs vs. Wolves
When considering size and robustness, the differences become clear in a wolf compared to a dog, as wolves are generally larger and more robust than most domestic dog breeds. Adult gray canines typically weigh between 70 to 145 pounds and stand 26 to 33 inches tall at the shoulder. In contrast, our beloved household canines come in a delightful variety of sizes. For instance, Great Danes can surpass wild canids in both height and weight, while smaller breeds like Chihuahuas are significantly diminutive, reminding us of the unique charm each pet brings to our lives.
Wolves are characterized by their narrower chests, longer legs, and more pronounced muzzles—adaptations that enhance their running and hunting capabilities in the wild. Their larger and stronger skulls and jaws are optimized for capturing and processing prey. On the other hand, the physical traits of dogs vary widely due to selective breeding, resulting in differences in ear shape, tail length, and coat type. This diversity illustrates their roles as cherished companions and hardworking animals, sharply contrasting with the survival-oriented adaptations observed in the wolf compared to a dog.
Furthermore, wolves display communal structures by living in packs, which play a crucial role in their hunting strategies and overall survival. Current studies continue to explore these size variations and the genetic links between dog breeds and their wild ancestors, specifically focusing on the wolf compared to a dog. This ongoing research further illuminates the fascinating relationship between these two species, reminding us of the deep connections we share with our furry family members. At Adventure Den, we are here to support you in nurturing your pets, ensuring they thrive in a loving environment.
Behavioral Traits: Socialization and Communication
Wolves uphold strict hierarchical structures within their packs, which are crucial for their survival in the wild. They communicate through a combination of vocalizations, body language, and scent marking, relying heavily on these methods to maintain order and cohesion within the pack. Wolves also exhibit social behaviors, such as caring for injured companions, which highlights their complex social dynamics.
In comparison, your furry family members, canines, have developed to be more sociable and adaptable to environments created by people, much like the difference seen in a wolf compared to a dog. They demonstrate a broader variety of vocalizations, including barking, whining, and howling, fulfilling different roles in communicating with both people and other dogs. Studies show that canine pups (n = 44) are more drawn to people than wild canines (n = 37), highlighting the considerable effect of domestication on their interaction abilities and communication techniques.
Dogs are also more attuned to people’s gestures and emotions, demonstrating a unique ability to interpret interpersonal cues. This flexibility has made canines more trainable and responsive to commands, a quality that is less evident in canids, who are less dependent on people for their relational needs. As noted by Tamás Faragó, comparing the vocal repertoires of canines, particularly the wolf compared to a dog, and their wild counterparts can provide intriguing insights into their communication methods, further distinguishing their dynamics.
At Adventure Den, we understand the importance of nurturing environments for your pets, where their social needs and communication styles can flourish.
Impact of Domestication on Behavior and Dependency
Domestication has profoundly transformed the behavior of our beloved canines, fostering a deep reliance on humans for social interaction, care, and emotional support. Unlike their wild counterparts, canines have developed a remarkable dependency on their caretakers, showcasing their need for companionship and approval. This attachment is evident in their actions; dogs actively seek out human connection, displaying affectionate behaviors that are far less common in wolves.
Studies reveal that canines excel in assessments of companionship and nurturance, often outperforming their closest relatives, which highlights their unique bond with people. Furthermore, these loyal companions have enhanced their cognitive abilities, particularly in understanding human commands and social cues, solidifying their roles as cherished companions and working partners. While wolves thrive in the wild, relying on instinct and pack dynamics, dogs have beautifully adapted to our human-dominated world, with their dependency becoming a defining characteristic of their loving nature.
At Adventure Den, we understand the importance of nurturing this bond. We invite you to explore how we can support your furry family members in a nurturing environment, ensuring they receive the care and companionship they deserve. Together, we can create a fulfilling life for your pets, where their needs are met with compassion and understanding.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between wolves and dogs not only illuminates their evolutionary paths but also highlights the profound impact of domestication on behavior, communication, and physical characteristics. While both species share a common ancestry, their adaptations to different environments have led to significant differences, especially in their social structures and interactions with humans. Dogs, having evolved alongside people, exhibit remarkable sociability and dependence, contrasting sharply with the autonomy and survival instincts that define wolves.
As we explore their physical traits, social behaviors, and communication styles, it becomes clear that the domestication of dogs has resulted in unique adaptations that enhance their roles as beloved companions. From their ability to interpret human emotions to their diverse vocalizations, dogs have developed skills that foster a deep bond with their human caretakers. In contrast, wolves maintain their wild instincts, relying on pack dynamics for survival and showcasing behaviors that are less influenced by human interaction.
Recognizing these differences is essential for nurturing the relationship between humans and their canine companions. By understanding the behavioral needs and communication styles of dogs, we can create more fulfilling interactions and a supportive environment for their growth. As the bond between species continues to evolve, appreciating these distinctions enriches our lives and ensures that we provide the love and care that our furry family members deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the common ancestor of dogs and wolves?
Dogs (Canis lupus familiaris) and wolves (Canis lupus) share a common ancestor, which highlights their connection despite the significant differences that have evolved over thousands of years of domestication.
How have dogs and wolves diverged over time?
Over time, dogs and wolves have adapted to their unique environments, leading to differences in behaviors, community structures, and physical traits that reflect their distinct lifestyles.
What is the social structure of wolves compared to dogs?
Wolves maintain strict pack hierarchies that are crucial for their survival, whereas dogs have adapted to more flexible roles within human households, becoming more dependent on humans for interaction and care.
How do dogs and wolves differ in their ability to connect with humans?
Dogs have developed a distinctive ability to connect with people, a skill that is less pronounced in wolves, who rely more on instinct and group dynamics.
What is the difference in brain size between dogs and wolves?
Research shows that tamed canines exhibit smaller relative brain sizes compared to wolves. The absolute brain size of wolves is about 24.32% larger than that of dogs with similar body mass.
How has domestication affected canine communication skills?
Domestication has enhanced dogs’ communication abilities with humans, emphasizing the cognitive differences between the two species and highlighting the special bond pets share with their owners.
Why is it important to understand the differences between dogs and wolves?
Understanding these differences can help create a nurturing environment for dogs, ensuring they thrive in our care and reinforcing the unique relationship they have with humans.







