Wolf vs Dog: Key Differences in Behavior and Adaptation
Overview
Wolves and dogs, though closely related, exhibit significant differences in behavior and adaptation, shaped by their unique evolutionary journeys. Wolves retain their wild instincts and pack hierarchies, while dogs have evolved to be more sociable and reliant on humans. This distinction is particularly important for pet owners who care deeply about their furry family members.
The process of domestication has favored traits in dogs that enhance their ability to thrive alongside people, fostering a nurturing environment where they can flourish. In contrast, wolves rely on survival strategies and natural instincts that are essential for their existence in the wild. Understanding these differences can help us provide the best care for our beloved pets, ensuring they feel safe and loved in our homes.
At Adventure Den, we celebrate these unique qualities of dogs and strive to create a space where they can express their sociable nature while feeling secure. By acknowledging their needs and instincts, we can nurture their well-being and strengthen the bond we share with them. Let’s embrace the journey of pet ownership together, ensuring that every moment spent with our pets is filled with love and understanding.
Introduction
The intricate relationship between wolves and dogs reveals a fascinating tapestry of evolution, behavior, and adaptation that speaks to the hearts of pet owners. Both species share a common ancestor and an impressive 99.9% genetic similarity, yet their paths have diverged dramatically due to domestication and environmental influences.
This article gently explores the key differences in behavior and adaptation between these two captivating canids. While wolves maintain their wild instincts, dogs have evolved to thrive alongside humans, becoming beloved members of our families.
What drives these differences, and how do they shape our understanding of these remarkable animals? Join us on this journey to discover how we can nurture our furry family members in a loving environment.
Defining Wolves and Dogs: Key Characteristics and Classifications
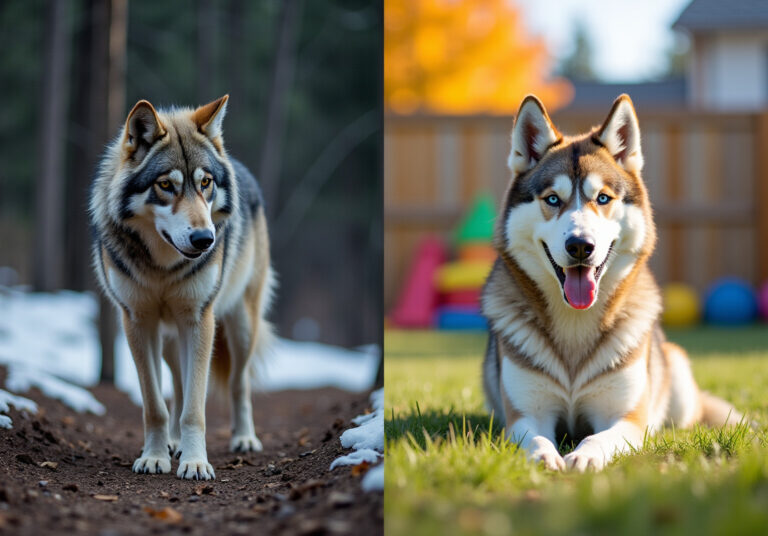
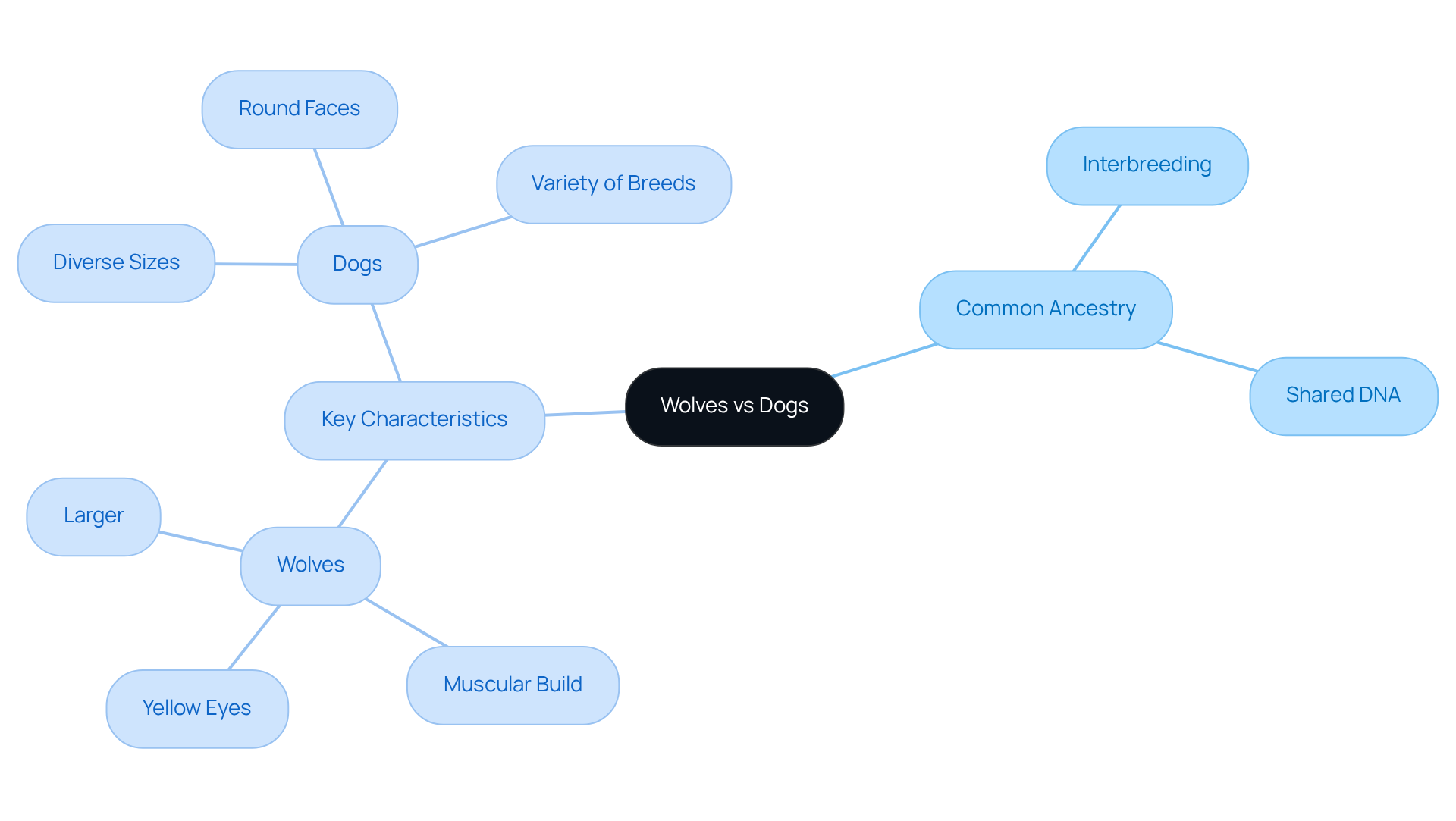
The relationship of wolf vs dog is highlighted by the fact that they share a common ancestor and can interbreed, producing fertile offspring. Yet, the differences in characteristics between the wolf vs dog define their classifications. Wolves are typically larger, boasting a more muscular build, longer legs, and narrower chests—adaptations that enhance their endurance and hunting capabilities in the wild. With their striking yellow eyes and pronounced muzzles, they are perfectly equipped for their predatory lifestyle.
In contrast, domestic canines show remarkable diversity in size and shape, often characterized by rounder faces and larger eyes. This variety reflects the extensive selective breeding that has occurred over thousands of years. As a result, we see an array of physical traits, from the compact frame of a bulldog to the slender build of a greyhound. Significantly, while canines and their wild relatives share over 90% of the same DNA, nearly all genes responsible for variation in contemporary canine breeds were present in the ancestral wild population.
Understanding these classifications is crucial for pet owners, as it lays the groundwork for analyzing behaviors and adaptations in various environments. For instance, the domestication process likely favored less aggressive canines that were more inclined to approach people for food. This has led to the friendly and sociable nature of our beloved pets. This divergence highlights the profound influence humans have had on the development of domestic canines, emphasizing the differences in wolf vs dog, and reminding us to appreciate both their common ancestry and their unique adaptations.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that in the wolf vs dog comparison, wolves are not meant to be kept as companions, while canines have rightfully earned the title of man’s best friend. This distinction underscores the behavioral differences between the two species, emphasizing the nurturing environment we strive to provide for your furry family members.
Exploring Genetics: The Genetic Makeup of Wolves and Dogs
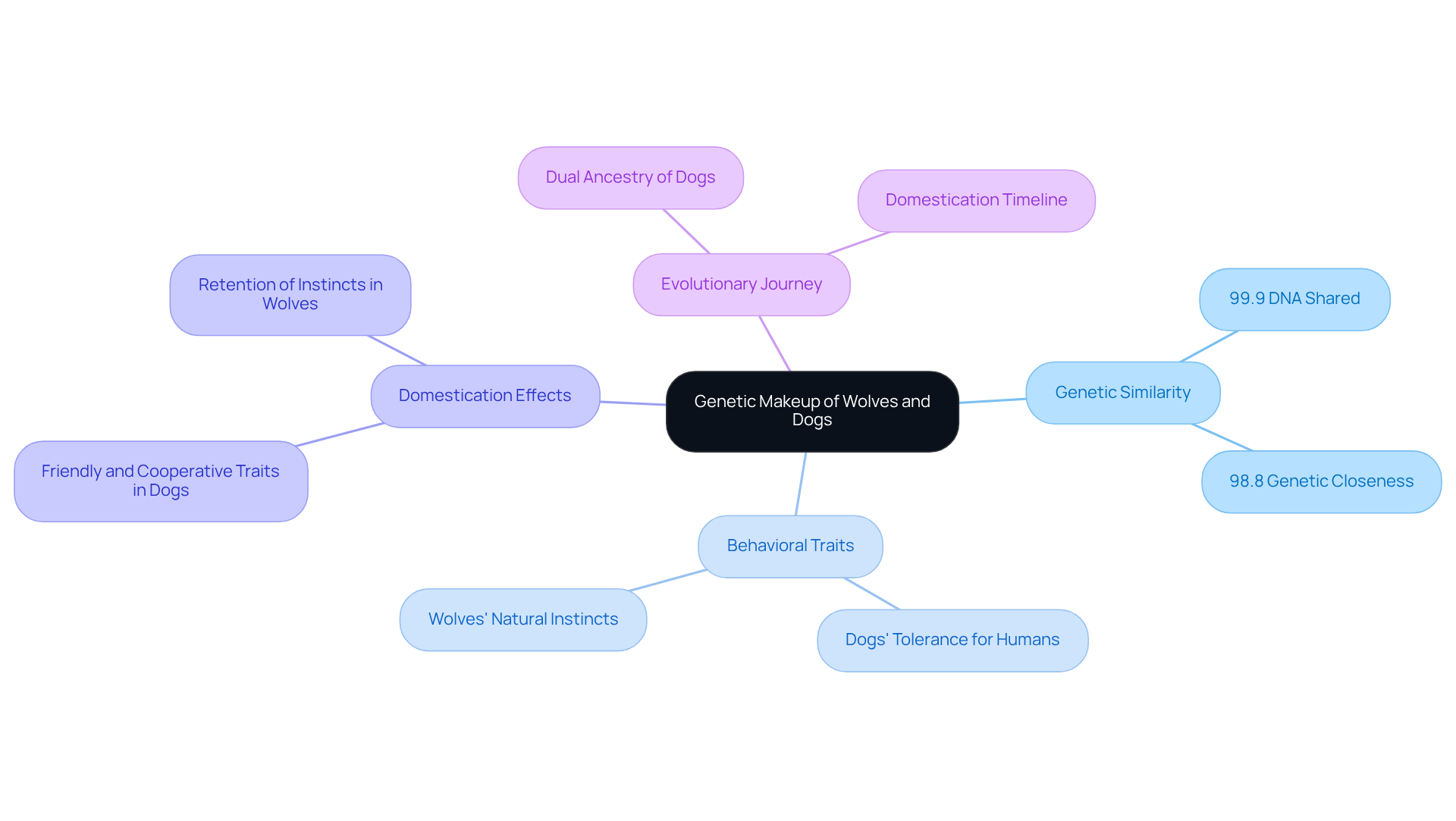
In the debate of wolf vs dog, it is noteworthy that they share an astonishing 99.9% of their DNA, showcasing a remarkable genetic bond that allows for interbreeding. However, the offspring often exhibit traits that are more aligned with one parent species. This genetic closeness is further highlighted by the fact that they share about 98.8% of their genetics, which is particularly evident in the wolf vs dog comparison, as noted by Annie Lennon from Labroots. While both species have similar chromosome counts, the journey of domestication has led to significant behavioral and physiological changes in our beloved canines.
For instance, dogs have developed a greater tolerance for interacting with people and enjoy a more varied diet, adapting beautifully to life alongside us. In contrast, the comparison of wolf vs dog highlights how wolves have retained their natural instincts and behaviors, which are essential for their survival in the wild. Dr. Anders Bergström emphasizes the fascinating bond that humans formed with wolves during the Ice Age, a relationship that was pivotal in understanding the wolf vs dog domestication process.
Moreover, canines have cultivated friendly and cooperative traits instead of fear and aggression when it comes to resource acquisition. This transformation underscores the profound effects of domestication. Understanding these genetic connections not only highlights the unique characteristics of each species but also reveals the distinctive physical traits that canines have developed, such as larger eyes that enhance communication.
Recent studies suggest that canines may have emerged from two distinct groups of canids, including ancient Siberian canids and western grey canids. This insight offers a deeper understanding of their evolutionary journey and the nurturing environment we strive to create for our furry family members.
Behavioral Analysis: Comparing Natural Instincts and Domestication Effects
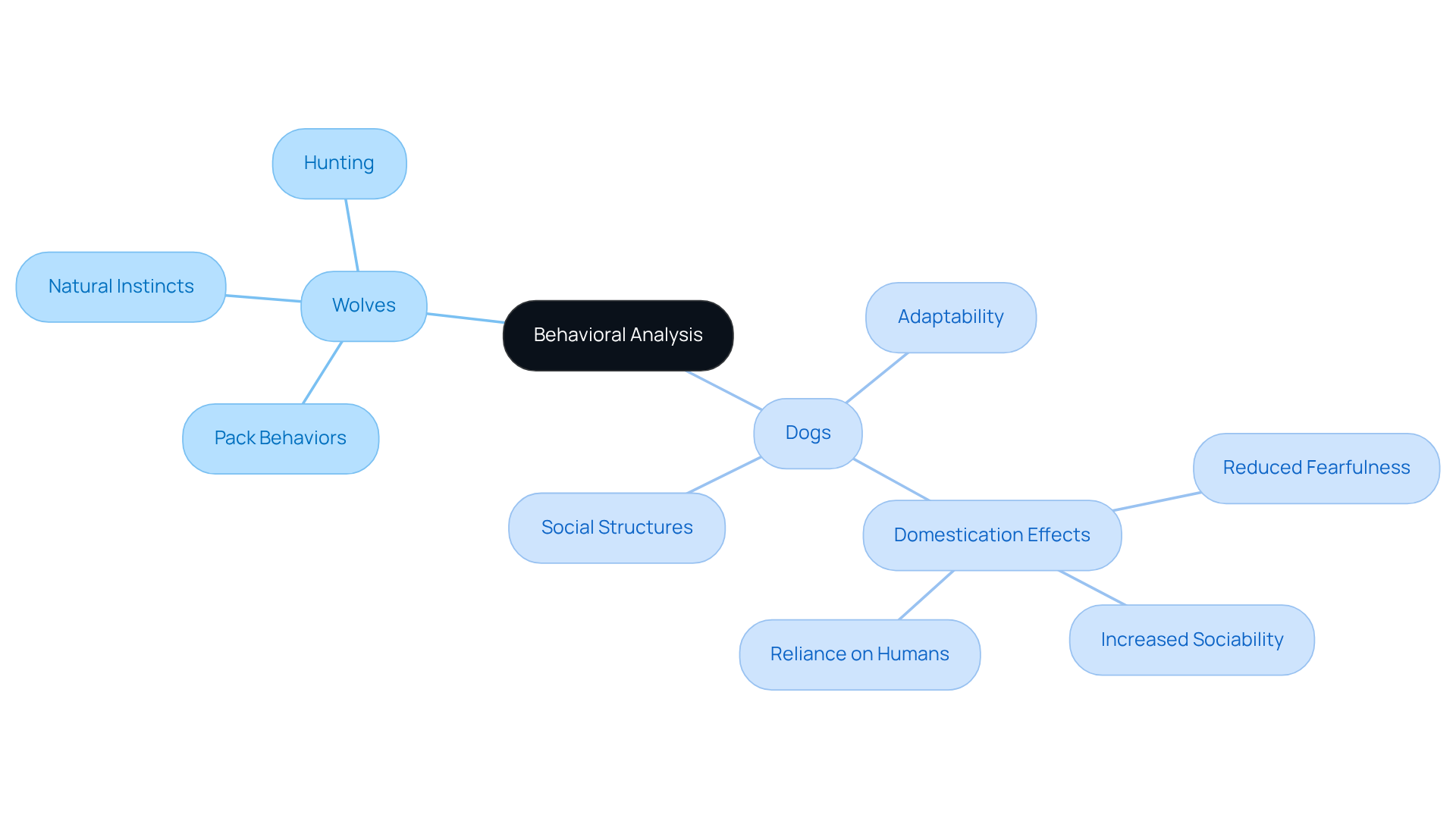
Wolves, with their strong pack behaviors, exemplify the importance of strict hierarchies for survival, which plays a crucial role in hunting and nurturing their young. Their natural instincts compel them to remain cautious, aggressive, and highly aware of their surroundings. On the other hand, our beloved household canines have adapted to more flexible social structures, often seeking companionship and support from humans. This transformation is largely a result of the domestication process, which has favored traits like sociability and reduced fearfulness.
For instance, your furry family members tend to be less hostile and more spirited than their wild counterparts, showcasing their ability to thrive in populated areas. While canines still possess a strong prey drive, many have lost the efficiency to hunt, relying instead on their human companions for sustenance. This behavioral insight highlights the profound impact of domestication on the instincts and social interactions of both species, particularly in the context of wolf vs dog. At Adventure Den, we understand these dynamics and are committed to providing a nurturing environment that caters to the unique needs of your pets.
Adaptation Strategies: How Wolves and Dogs Thrive in Different Environments
Wolves are remarkably adaptable animals, thriving in a variety of ecosystems, including forests, tundras, and grasslands. Their adaptations include thick fur for insulation against harsh climates and an acute sense of smell that aids in hunting. Socially, wolves often hunt in packs, employing coordinated strategies to take down larger prey, which is crucial for their survival in the wild.
In contrast, our beloved domestic dogs have evolved to flourish in various environments shaped by people, from bustling urban areas to tranquil rural settings. Their ability to forge strong connections with individuals has been vital, allowing them to depend on us for food, shelter, and companionship. Dogs exhibit a wide array of behaviors that highlight their adaptability, including the modification of vocalizations and body language to communicate effectively with humans.
This comparison of wolf vs dog underscores their differing adaptation strategies, revealing their unique methods of survival in varying environments. At Adventure Den, we understand the importance of nurturing these connections, ensuring that your furry family members thrive in a loving and supportive atmosphere. Together, we can create a nurturing environment that caters to the needs of your pets, allowing them to flourish just as they were meant to.
Conclusion
The comparison between wolves and dogs reveals a fascinating interplay of evolution, behavior, and adaptation that resonates deeply with pet owners. While both species share a common ancestor and possess striking genetic similarities, their paths diverged significantly due to domestication and environmental influences. Wolves, with their wild instincts and social hierarchies, embody the essence of survival in nature. In contrast, domestic dogs have transformed into affectionate companions, reflecting the profound impact humans have had on their development.
Throughout this exploration, we uncover key differences in:
- Physical characteristics
- Genetic makeup
- Behavioral traits
Wolves exhibit adaptations that enhance their hunting capabilities and survival instincts, thriving in diverse ecosystems. On the other hand, dogs have evolved to live harmoniously alongside humans, showcasing their remarkable ability to adapt to various environments and social structures. These insights emphasize how domestication has shaped the friendly and sociable nature of dogs, setting them apart from their wild relatives.
Ultimately, recognizing the distinctions between wolves and dogs is essential not only for understanding their unique adaptations but also for appreciating the roles they play in our lives. This knowledge encourages responsible pet ownership and fosters a deeper respect for the natural world. By nurturing the bond with your furry family members while acknowledging their wild ancestry, a more harmonious relationship can be cultivated, benefiting both you and your beloved companions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between wolves and dogs?
Wolves and dogs share a common ancestor and can interbreed, producing fertile offspring.
What are the key physical differences between wolves and dogs?
Wolves are typically larger, with a more muscular build, longer legs, and narrower chests, which enhance their endurance and hunting capabilities. In contrast, domestic dogs exhibit remarkable diversity in size and shape, often characterized by rounder faces and larger eyes due to extensive selective breeding.
How much DNA do wolves and dogs share?
Wolves and domestic canines share over 90% of the same DNA.
What has influenced the physical traits of domestic dogs?
The extensive selective breeding that has occurred over thousands of years has led to a variety of physical traits in domestic dogs, from the compact frame of a bulldog to the slender build of a greyhound.
How does the domestication process affect canine behavior?
The domestication process likely favored less aggressive canines that were more inclined to approach people for food, resulting in the friendly and sociable nature of domestic dogs.
Why are wolves not suitable as companions?
Wolves are not meant to be kept as companions due to their behavioral differences compared to domestic dogs, which have been bred to be more sociable and friendly toward humans.
What does the classification of wolves and dogs signify for pet owners?
Understanding the classifications of wolves and dogs is crucial for pet owners as it helps analyze behaviors and adaptations in various environments, emphasizing the nurturing environment needed for domestic canines.







